How to operate a drone? This seemingly simple question opens a world of exciting possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to efficient surveying. Mastering drone operation, however, requires a blend of technical understanding and responsible practice. This guide will equip you with the knowledge and skills to safely and effectively pilot your drone, from pre-flight checks to post-flight maintenance, covering everything from basic controls to advanced maneuvering techniques.
We’ll explore flight planning, camera operation, and legal considerations, ensuring you’re prepared for a smooth and enjoyable flight experience.
We’ll delve into the intricacies of drone controls, explaining the functions of throttle, yaw, pitch, and roll using clear analogies. Different flight modes, such as GPS and attitude modes, will be discussed, highlighting their respective benefits and drawbacks. We’ll also guide you through a step-by-step process for takeoff, hovering, and landing, ensuring a confident start to your drone journey.
Beyond the basics, we’ll explore advanced techniques, camera operation, and essential maintenance procedures to maximize your drone’s lifespan and performance.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
Before you even think about taking off, a thorough pre-flight check is crucial for a safe and successful drone flight. This involves inspecting key components, verifying signal strength, and familiarizing yourself with emergency procedures. Neglecting this step can lead to accidents and damage to your drone or property.
Pre-Flight Inspection
A comprehensive pre-flight inspection ensures your drone is in optimal condition. This includes checking the battery level (ideally, fully charged), carefully examining the propellers for any damage or debris, and verifying a strong GPS signal. Weak GPS signals can lead to erratic flight behavior or complete loss of control.
Pre-Flight Safety Check Procedure
The pre-flight safety check should be a methodical process. Begin by visually inspecting the drone body for any cracks or damage. Then, check each propeller for damage, ensuring they are securely attached. Next, verify the battery is fully charged and properly connected. Finally, move to an open area with a clear view of the sky to ensure a strong GPS signal.
Pre-Flight Checklist
| Model | Check Item | Pass/Fail | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| All Drone Models | Battery Level | Minimum 80% recommended | |
| All Drone Models | Propeller Inspection | Check for cracks, bends, or damage | |
| All Drone Models | GPS Signal Strength | Ensure at least 8 satellites are locked | |
| All Drone Models | Gimbal Functionality | Test gimbal movement | |
| All Drone Models | Visual Inspection of Drone Body | Check for damage or loose parts | |
| All Drone Models | Controller Battery Level | Ensure controller is fully charged | |
| All Drone Models | Firmware Update | Ensure drone is running the latest firmware |
Emergency Procedures
Knowing how to handle emergencies is critical. In case of signal loss, most drones have a “return-to-home” (RTH) function. This feature will automatically guide the drone back to its takeoff point. If a malfunction occurs, immediately attempt to land the drone safely in a clear area. If the drone is unresponsive, your only option is to power it down, which can sometimes be done through the controller or by using the battery removal procedure Artikeld in the drone’s manual.
Understanding Drone Controls and Navigation
Mastering drone controls is essential for safe and effective operation. Understanding the basic commands and different flight modes allows for precise maneuvering and avoids potential accidents.
Basic Drone Controls
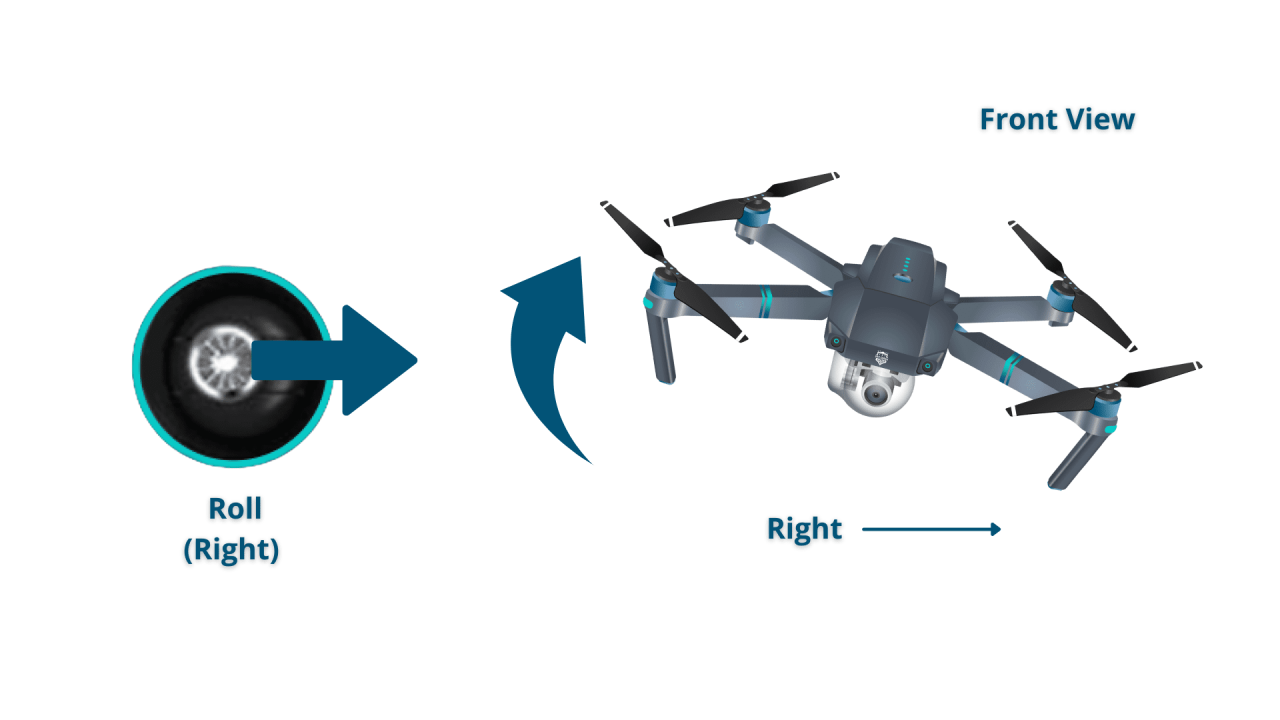
Most drones use four basic controls: throttle (up and down), yaw (rotation), pitch (forward and backward tilt), and roll (side-to-side tilt). Think of it like this: throttle controls altitude, yaw controls turning, pitch controls forward and backward movement, and roll controls sideways movement. These controls work in conjunction to allow for a variety of flight maneuvers.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires careful planning and adherence to regulations. For a comprehensive guide covering all aspects, from basic controls to advanced maneuvers, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone and become proficient in safe and responsible drone piloting.
This will ensure your flights are both successful and compliant.
Flight Modes
Different flight modes offer varying levels of control and stability. GPS mode uses satellite data for stable flight, ideal for beginners. Attitude mode relies on the drone’s internal sensors, offering more agility but less stability. Manual mode provides full control, best for experienced pilots.
- GPS Mode: Stable and easy to use, ideal for beginners.
- Attitude Mode: More agile but requires more skill.
- Manual Mode: Full control, for experienced pilots only.
Controller Types
Controllers vary in design and functionality. Joystick controllers provide precise control and are generally preferred by experienced pilots. Touchscreen controllers offer a more intuitive interface, but may be less precise.
- Joystick Controllers: Precise control, preferred by experienced pilots.
- Touchscreen Controllers: Intuitive interface, may be less precise.
Step-by-Step Takeoff, Hover, and Landing
- Power on the drone and controller, ensuring a strong GPS signal.
- Calibrate the compass and IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit) as instructed by your drone’s manual.
- Slowly increase the throttle to lift the drone off the ground.
- Use the pitch and roll controls to maintain a stable hover.
- Slowly decrease the throttle to gently lower the drone to the ground for landing.
- Power off the drone and controller.
Flight Planning and Maneuvering: How To Operate A Drone
Careful flight planning is essential for safe and efficient drone operation. This involves considering weather conditions, airspace restrictions, and potential obstacles to ensure a smooth and successful flight.
Flight Planning Importance
Flight planning minimizes risks and ensures compliance with regulations. Before each flight, check the weather forecast for wind speed and direction, rain, or fog. Identify potential airspace restrictions and no-fly zones using online resources like FAA’s B4UFLY app (for US users) or similar apps for your region. Inspect the flight area for obstacles such as trees, buildings, or power lines.
Sample Flight Plan for Beginners
A simple flight plan might involve taking off from a designated point, hovering at a low altitude (e.g., 10 meters), flying in a square pattern covering a small area, and then returning to the takeoff point for landing. This allows you to practice basic controls and maneuvers in a controlled environment.
Basic Drone Maneuvers
Basic maneuvers include turns, ascents, descents, and sideways movements. Smooth and precise movements are achieved through careful control of the pitch, roll, and yaw controls. Practice these maneuvers in a safe and open area before attempting more complex flights.
Tips for Smooth and Precise Movements
Use small, controlled movements of the joysticks or touchscreen controls. Avoid jerky movements, which can destabilize the drone. Practice hovering in place to improve your control and stability. Use the drone’s assisted flight modes (if available) to aid in stability and precision.
Drone Camera Operation and Photography/Videography
Capturing stunning aerial photos and videos requires understanding your drone’s camera settings and mastering different camera angles and shot types.
Camera Settings and Image Quality
Understanding camera settings like aperture, shutter speed, and ISO is key to high-quality imagery. Aperture controls the amount of light entering the lens, affecting depth of field. Shutter speed determines how long the sensor is exposed to light, influencing motion blur. ISO measures the sensor’s sensitivity to light, affecting image noise.
Adjusting Camera Settings for Different Lighting
In bright sunlight, you’ll likely need a faster shutter speed and lower ISO to prevent overexposure and reduce noise. In low-light conditions, a slower shutter speed and higher ISO may be necessary, but be mindful of increased noise. Experiment with different settings to find the optimal balance for various lighting scenarios.
Camera Angles and Shots
Different camera angles create unique perspectives. Aerial shots provide a bird’s-eye view, close-ups capture fine details, and tracking shots follow a moving subject. Experiment with different angles and shots to find what best suits your creative vision.
Comparison of Drone Camera Features
| Model | Camera Resolution (Stills) | Sensor Size | Video Resolution | Frame Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Example Drone A | 12MP | 1/2.3″ | 4K | 60fps |
| Example Drone B | 20MP | 1/1.7″ | 4K | 120fps |
| Example Drone C | 48MP | 1″ | 6K | 60fps |
Post-Flight Procedures and Drone Maintenance
Proper post-flight procedures and regular maintenance are crucial for extending the lifespan of your drone and ensuring its continued safe operation.
Landing and Storage Procedures
After a flight, land the drone gently in a safe area, away from obstacles. Power down the drone and controller, and store them in a safe, dry place, protecting them from dust and moisture. Always store the batteries separately and follow the manufacturer’s instructions for safe battery storage.
Routine Maintenance Tasks
Regular maintenance involves cleaning the drone body and propellers with a soft cloth, inspecting for any damage, and checking the battery connections. Tighten any loose screws or components as needed. Inspect the gimbal and camera for any signs of damage or misalignment.
Battery Care and Storage
Proper battery care is essential for maximizing battery lifespan. Avoid fully discharging or overcharging batteries. Store batteries in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight or extreme temperatures. Always follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for battery storage and charging.
Regular Drone Maintenance Schedule
A monthly inspection should include a thorough visual inspection of the drone, propellers, and gimbal. Every three months, consider a more in-depth inspection, including cleaning the drone thoroughly and checking for any signs of wear and tear. Battery calibration and firmware updates should be done as needed, based on manufacturer’s recommendations.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance

Understanding and adhering to local drone regulations is essential for responsible drone operation and avoiding legal issues. These regulations vary by country and region, so it’s crucial to research the specific rules in your area.
Importance of Adhering to Regulations
Ignoring drone regulations can lead to fines, legal penalties, and even criminal charges. Familiarize yourself with local laws regarding drone registration, airspace restrictions, and operational limitations before flying.
Airspace Restrictions and No-Fly Zones
Many areas have restricted airspace, including airports, military bases, and national parks. These areas are often marked on online maps and apps. Always check for airspace restrictions before planning a flight.
Obtaining Necessary Permits or Licenses, How to operate a drone
In some areas, you may need to obtain permits or licenses before operating a drone, especially for commercial purposes or flights in sensitive areas. Check with your local aviation authority for specific requirements.
Responsible Drone Operation Practices

Responsible drone operation includes respecting the privacy of others, avoiding flying over crowds, and keeping the drone within visual line of sight. Always be mindful of the environment and avoid disturbing wildlife or causing damage to property.
Troubleshooting Common Drone Issues
Even with careful planning and maintenance, drone issues can occur. Knowing how to troubleshoot common problems can save time and frustration.
Common Drone Problems
Common problems include low battery, GPS signal loss, motor failure, and controller connectivity issues. Each of these requires a different troubleshooting approach.
Troubleshooting Steps
For low battery, charge the battery fully. For GPS signal loss, move to an open area with a clear view of the sky. For motor failure, inspect the motors for damage and ensure proper connections. For controller connectivity issues, check the batteries in both the drone and the controller and ensure proper pairing.
Troubleshooting Flowchart
A flowchart would visually guide users through the troubleshooting process, starting with identifying the problem, then moving to specific steps based on the issue, leading to solutions or further diagnostics.
(Note: A visual flowchart would be included here in a real article. Due to the limitations of this text-based format, a detailed textual description is not practical.)
Tips for Preventing Common Drone Issues
Regular maintenance, proper battery care, and avoiding extreme weather conditions can significantly reduce the likelihood of common drone issues. Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions for operation and maintenance.
Operating a drone is a rewarding experience that blends technology and skill. By diligently following pre-flight checklists, understanding drone controls, and adhering to safety regulations, you can unlock the full potential of your drone. Remember, responsible drone operation is paramount; prioritizing safety and legal compliance ensures a positive and sustainable future for this exciting technology. This guide has provided a foundation for your drone journey; now, it’s time to take to the skies responsibly and capture your own unique perspective.
Query Resolution
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones with GPS stabilization and automatic return-to-home features are ideal for beginners. Research models known for their ease of use and robust safety features.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires a good grasp of regulations and safe flying practices. For a comprehensive guide covering all aspects, including practical exercises, you can check out this helpful resource on how to operate a drone. Ultimately, responsible and proficient drone operation is all about practice and understanding the technology.
Compass calibration should be performed before each flight, especially if you’ve moved to a new location or experienced any significant impacts.
What should I do if my drone loses GPS signal?
Most drones have a “return-to-home” function. If available, activate it. Otherwise, carefully attempt to manually control the drone back to your location, prioritizing safety.
How do I store my drone batteries safely?
Store batteries in a cool, dry place away from flammable materials. Avoid fully charging or fully discharging them for extended periods.
